hermes and lipid transport | Cholesterol transport between cellular membranes: A balancing hermes and lipid transport SLCs are membrane proteins that transport metabolites across lipid membranes and play an important role in a variety of biological processes. The SLC superfamily consists . CCC atrašanās vieta. CCC Grupa ir viena no lielākajiem apavu mazumtirgotājiem Centrāleiropā, ka arī viena no Eiropas lielākajiem apavu ražotājiem. Ar meitasuzņēmuma eob.
0 · The proton
1 · The Proton
2 · Structure–function insights into direct lipid transfer between
3 · Non
4 · Lipid transfer proteins: the lipid commute via shuttles, bridges and
5 · ERMES — from myths to molecules
6 · Cholesterol transport between cellular membranes: A balancing
7 · Advances on the Transfer of Lipids by Lipid Transfer Proteins
8 · A novel superfamily of bridge
Left ventricular (LV) remodeling and hypertrophy are associated with the development of congestive heart failure (CHF) and an increased incidence of other major cardiovascular events, including sudden death. 1–4 LV remodeling may be produced by various physiological and pathological mechanisms.
By studying developmentally programmed cell death, we identified hermes, which encodes a monocarboxylate transporter that participates in Eiger (TNF)-triggered and . SLCs are membrane proteins that transport metabolites across lipid membranes and play an important role in a variety of biological processes. The SLC superfamily consists . Lipid-transfer proteins (LTPs), which regulate diverse lipid-mediated cellular processes and accelerate vectorial transport of lipid monomers between membranes in vitro, .Transfer of lipid across the cytoplasm is an essential process for intracellular lipid traffic. Lipid transfer proteins (LTPs) are defined by highly controlled in vitro experiments. The functional .
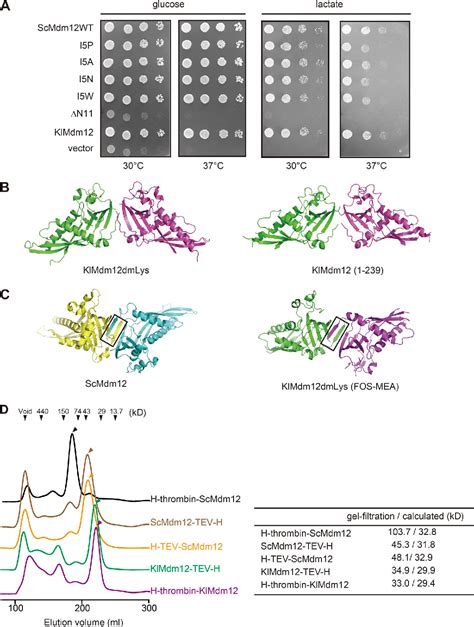
Mutations in Mmm1 or Mdm12 impaired the lipid transfer activities of the Mdm12–Mmm1 complex and furthermore caused defective phosphatidylserine transport from .Instead, the bulk of lipid traffic is mediated by a large group of lipid transfer proteins (LTPs), which move small numbers of lipids at a time using hydrophobic cavities that stabilize lipid molecules .
Lipid transfer proteins mediate nonvesicular transport of lipids at membrane contact sites to regulate the lipid composition of organelle membranes. Recently, a new type of bridge-like lipid transfer protein has . Cholesterol can be lifted from the bilayer to the aqueous, cytosolic environment with the help of lipid transfer proteins (LTPs) whose hydrophobic cavity shields the lipid from .
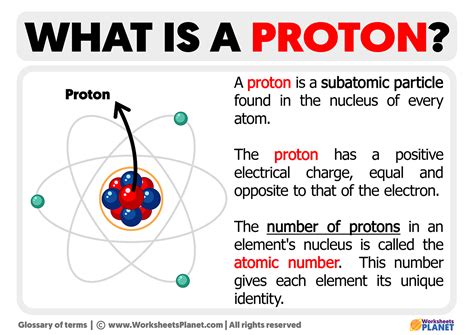
HDL participates in reverse cholesterol transport, which is the transport of cholesterol back to the liver. HDL picks up cholesterol from tissues/blood vessels and returns it to the liver itself or transfers it to other lipoproteins returning to the liver. Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\): HDL is involved in reverse cholesterol transport Endogenous pathway. 1.Fat and cholesterol arriving at the liver are repackaged into VLDLs.. 2.VLDLs enter the bloodstream between meals and travel to the peripheral tissues.. 3.VLDLs meet tissues expressing lipoprotein lipase (e.g. muscle and adipose tissue) and release their glycerol and fatty acids.. 4.After a VLDL has unloaded most of its fats it becomes smaller . Cholesterol is the most abundant single lipid in mammalian cells. Ikonen and Zhou discuss major exo-and endocytic cholesterol transport routes and how lipid transfer proteins at membrane contacts and membrane transport intersect along these routes. They discuss co-transport of cholesterol with other lipids as well as physiological relevance.
Hermes is the leading expert for integrated solutions along the supply chain and a partner for national and international trading companies. . That's why on the one hand we offer sufficient capacity for all means of transport to meet individual needs at short notice. On the other hand we put your individual goals into focus: We offer services .Lipid assembly into cell membranes. Dennis R. Voelker, in Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes (Fifth Edition), 2008 5 Future directions. Cellular lipid transport is a fundamental process essential to all cell growth, division, and differentiation. Our understanding of lipid transport has changed markedly in the last 5 years, during which the number of genes . Non-vesicular lipid transport between intracellular membranes can be mediated by spontaneous lipid transfer or lipid-transfer proteins (LTPs) and is crucial for maintaining the identities of .
In short, elevated LDL blood lipid profiles indicate an increased risk of heart attack, while elevated HDL blood lipid profiles indicate a reduced risk.The University of Maryland Medical Center reports that omega-3 fatty acids promote lower total cholesterol and lower triglycerides in people with high cholesterol. 3. Dietary lipids and de novo synthesized lipid by adipose tissue and liver must be transported between various tissues and organs for utilization and storage. Lipids are insoluble in water The problem arises of how to transport this non-polar molecules in aqueous environment (the blood) 6/9/2014 7:39:25 AM 3uploaded by elhadi hassan
Lipid transport may also be described in terms of the ‘forward’ and ‘reverse’ transport of cholesterol. In this case, ‘forward’ transport indicates the arrival of cholesterol in the blood from the gut (exogenous) and liver (endogenous) and carriage back to the liver, whereas ‘reverse’ transport (HDL pathway) is the movement of .
Describe the following passive transport processes: diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis. Explain the function of each in a cell. Describe and explain the effects (i.e., on cell size, cell shape, and cytosol solute concentrations) of placing red blood cells in a solution that is a) hypertonic relative to the cytosol, b) hypotonic relative to the cytosol, and c) Isotonic relative to . Transport of lipids across membranes is fundamental for diverse biological pathways in cells. Multiple ion-coupled transporters take part in lipid translocation, but their mechanisms remain . Because the lipid extraction and lipid insertion assays described in Fig. 4 do not allow evaluation of the kinetics of lipid transfer between membranes, we performed a fluorescent-based lipid transfer kinetics assay between membranes, which is similar to the PA or PS transport assay reported previously (Connerth et al., 2012; Watanabe et al .
The proton
This observation strongly suggested a role for ERMES in lipid transport between these organelles and motivated several laboratories to uncover the underlying molecular mechanism.
Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\): HDL is involved in reverse cholesterol transport. C represents cholesterol. ADAPT \(\PageIndex{6}\) You are probably familiar with HDL and LDL being referred to as "good cholesterol" and "bad cholesterol," respectively. This is an oversimplification to help the public interpret their blood lipid values, because . Only a minority of lipids achieve their final intracellular distribution through transport by vesicles. Instead, the bulk of lipid traffic is mediated by a large group of lipid transfer. The configuration of the subunits creates a near-continuous hydrophobic groove, allowing lipids to ‘slide’ from one membrane to the other, finally explaining how ERMES may facilitate lipid.
By studying developmentally programmed cell death, we identified hermes, which encodes a monocarboxylate transporter that participates in Eiger (TNF)-triggered and autophagic cell death. SLCs are membrane proteins that transport metabolites across lipid membranes and play an important role in a variety of biological processes.
SLCs are membrane proteins that transport metabolites across lipid membranes and play an important role in a variety of biological processes. The SLC superfamily consists of over 400 genes in humans, and 30% of those remain uncharacterized (Perland and . Lipid-transfer proteins (LTPs), which regulate diverse lipid-mediated cellular processes and accelerate vectorial transport of lipid monomers between membranes in vitro, could potentially.Transfer of lipid across the cytoplasm is an essential process for intracellular lipid traffic. Lipid transfer proteins (LTPs) are defined by highly controlled in vitro experiments. The functional relevance of these is supported by evidence for the same reactions inside cells. Mutations in Mmm1 or Mdm12 impaired the lipid transfer activities of the Mdm12–Mmm1 complex and furthermore caused defective phosphatidylserine transport from the ER to mitochondrial membranes via ERMES in vitro. Therefore, the Mmm1–Mdm12 complex functions as a minimal unit that mediates lipid transfer between membranes. Go to: Introduction.
Instead, the bulk of lipid traffic is mediated by a large group of lipid transfer proteins (LTPs), which move small numbers of lipids at a time using hydrophobic cavities that stabilize lipid molecules outside membranes. Lipid transfer proteins mediate nonvesicular transport of lipids at membrane contact sites to regulate the lipid composition of organelle membranes. Recently, a new type of bridge-like lipid transfer protein has emerged; these proteins contain a long hydrophobic groove and can mediate bulk transport of lipids between organelles.
The Proton
Flamingo Las Vegas radiates classic Vegas charm. There's no better place to take in Las Vegas than right in the heart of the Las Vegas Strip. The wildlife habitat, entertainment, oasis-style pools, world-class restaurants, and premium nightlife make Flamingo Las Vegas beyond fabulous.
hermes and lipid transport|Cholesterol transport between cellular membranes: A balancing